This guide to project accounting contains what you need to know to get started with Project Accounting if you are an Architecture, Engineering, Construction, Media, Professional Services, Consulting, or other business that works primarily in project delivery.
Discover the essential techniques and best practices for project accounting in architectural and engineering firms with our comprehensive guide to project accounting. Gain valuable insights into budgeting, cost management, billing, financial reporting, compliance, and more. Start optimizing your project accounting processes today!

Why Project Accounting Matters for A/E Firms
In architecture and engineering (A/E) firms, profitability doesn’t come from the firm’s bottom line—it comes from the performance of each individual project. That’s where project accounting comes in.
At Summit Business Advisors, we help A/E firms gain real financial control by applying project-level accounting best practices that align operations with strategy. If you're relying solely on general accounting tools, you're missing key insights that could transform your firm’s margins, resource planning, and decision-making.
What Makes Project Accounting Different?
Unlike traditional accounting, which looks at the business as a whole, project accounting tracks financials at the project level. It gives you a clear view into the profitability, resource usage, and financial performance of every project—so you’re not guessing where your profits (or losses) are coming from.
Core Components of Project Accounting
1. Focus on Individual Projects
Every project is tracked as its own profit center. You get visibility into how each engagement is performing—no more lumped-together financials that mask what's really going on.
2. Tracking Costs and Revenue in Real Time
From labor hours and materials to subcontractors and overhead, every cost is allocated directly to the project. Combined with accurate revenue tracking, this gives you true job-costing visibility—and the ability to adjust course quickly.
3. Monitoring Profitability
Know which projects are profitable and which are bleeding resources. With detailed job-by-job profitability data, you can improve pricing, evaluate client fit, and make better go/no-go decisions.
4. Project-Based Financial Reporting
Instead of waiting for a month-end report, project accounting provides up-to-date dashboards and reports for each project. Project managers and stakeholders stay informed and can spot financial issues before they become major problems.
5. Smarter Resource Allocation
See where your time, people, and budget are going—and how efficiently they’re being used. Project accounting helps you optimize workloads, prevent bottlenecks, and reduce overruns.
6. Better Decision-Making
With real-time financial data at the project level, you can make strategic decisions about scope changes, staffing, and budgeting based on facts—not assumptions.
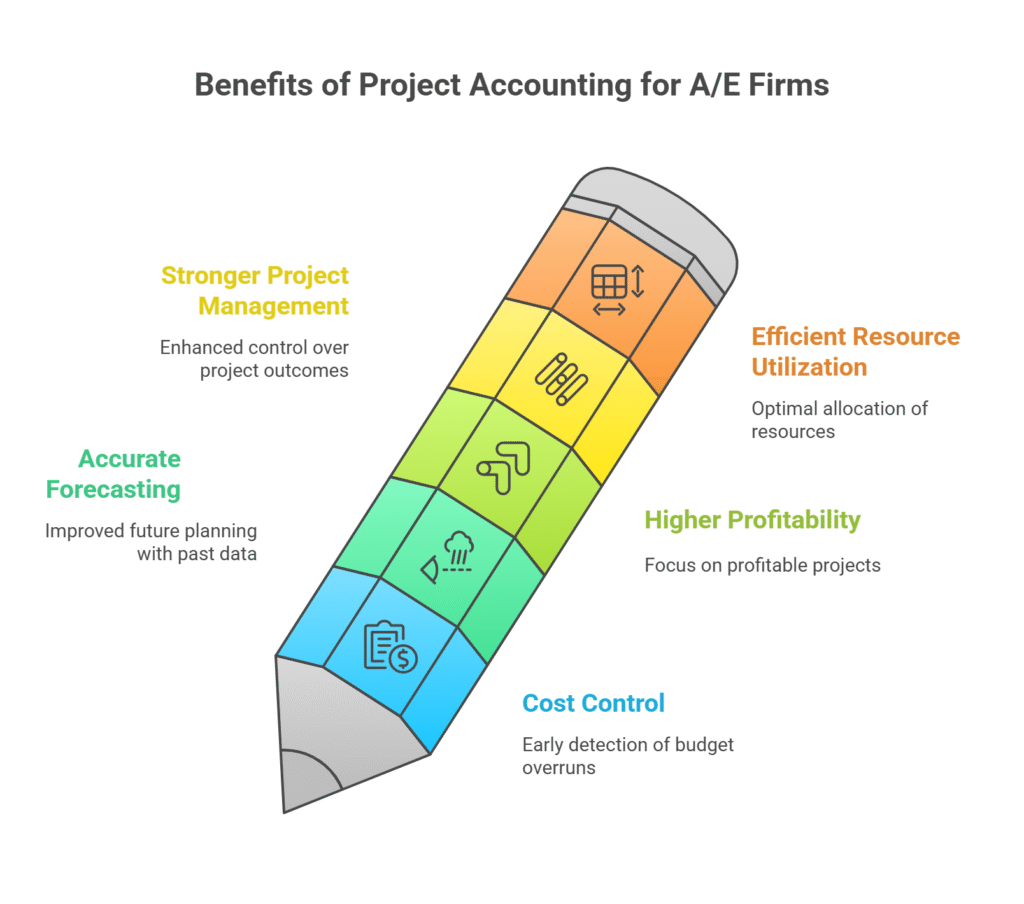
Why A/E Firms Rely on Project Accounting
✔️ Better Cost Control
Spot budget overruns early and take corrective action before profitability suffers.
✔️ More Accurate Forecasting
Use past project data to improve future planning, pricing, and proposals.
✔️ Higher Profitability
When you know which projects are generating margin—and which ones aren’t—you can focus your team where it counts.
✔️ Stronger Project Management
Equip your PMs with financial tools and reporting they can actually use. That means fewer surprises and more control over project outcomes.
✔️ More Efficient Resource Utilization
Stop overallocating high-cost resources or underusing key talent. Optimize your teams based on real project data.
Ready to Level Up Your Project Financials?
Project accounting isn't just for large firms or complex jobs. It's a practical, high-impact tool that helps every A/E firm improve profitability and operational control.
At Summit Business Advisors, we specialize in helping A/E leaders implement project accounting frameworks that are easy to manage and customized to how you actually run projects.
Let’s talk about how we can help you see your business more clearly—project by project.
I. Introduction to Project Accounting
Project accounting is a specialized branch of accounting that focuses on tracking and managing the financial aspects of individual projects within a company. Unlike traditional accounting, which looks at the overall financial health of a business, project accounting delves into the financial details of specific projects. It involves monitoring project costs, revenue, and profitability, as well as analyzing financial data to make informed decisions. Project accounting provides businesses, especially architectural and engineering firms, with a clearer understanding of the financial performance of each project and helps in identifying potential issues, ensuring projects stay within budget, and maximizing profitability.
In project accounting, each project is treated as a separate entity, with its own budget, expenses, and revenue. It allows businesses to allocate costs specifically to each project, including direct labor, materials, subcontractor expenses, and overheads. By closely tracking and managing project costs, project accounting enables businesses to identify areas of inefficiency, make necessary adjustments, and optimize resource allocation. This level of detailed financial analysis provides greater transparency and accountability, allowing businesses to better evaluate the profitability and viability of their projects. Overall, project accounting plays a crucial role in ensuring financial control, making informed decisions, and maximizing the success of architectural and engineering projects.

A. What is Project Accounting?
Unlike traditional accounting, which looks at the overall financial health of a business, project accounting delves into the financial details of specific projects.
B. Why project accounting is important for engineering, construction, and architectural firms
II. Guide to Project Accounting Basics
Project accounting is a specialized accounting approach that focuses on managing and tracking the financial aspects of individual projects within a company. It involves creating budgets, monitoring project costs and revenues, tracking project progress, and analyzing financial data to ensure projects stay within budget and meet financial goals. Project accounting provides businesses with a clearer understanding of the financial performance of each project, allowing for better decision-making and resource allocation. By treating each project as a separate entity, project accounting enables businesses, including architectural and engineering firms, to have better control over their projects' finances and ultimately improve profitability.
A. Types of project accounting
There are different types of project accounting methods that businesses can utilize based on their specific needs and requirements. Each type of project accounting offers distinct advantages and can be tailored to suit the unique needs of architectural and engineering firms.
Project accounting typically falls into two categories:
-
Internal Projects
These track costs tied to internal initiatives—such as system upgrades, training programs, or R&D efforts. The focus is on managing expenses and resource use within the business. -
External Projects
These involve client-facing work—where financials are tied to deliverables, timelines, and revenue recognition. External project accounting helps firms manage profitability, billing, and client expectations.
Both types require thoughtful cost tracking and tailored revenue recognition methods to ensure accuracy, compliance, and financial clarity.
B. Key components of project accounting
Revenue Recognition Methods
How and when you recognize revenue depends on the nature of the project:
-
Sales Basis: Revenue is recognized at the time of sale, regardless of payment status.
-
Installment Method: Revenue is recognized as client payments are received—common for longer-term contracts.
-
Percentage of Completion: Revenue aligns with project progress, ideal for phased, measurable work.
-
Cost Recovery: Revenue is only recognized after all project costs have been recovered—a conservative approach.
-
Completed Contract: Revenue is recorded only when the project is fully complete and deliverables are met.
Cost Management Fundamentals
-
Direct Costs: Labor, materials, equipment—expenses tied directly to a project.
-
Overhead Costs: Indirect costs like admin, rent, and utilities—allocated based on usage or proportion.
-
Budgeting: Establish detailed budgets upfront and monitor them throughout the project lifecycle.
-
Cost Allocation: Use tailored methods to assign costs—whether by direct tracking, resource usage, or percentages.
Project Accounting in Practice
Project accounting isn’t just bookkeeping—it’s a performance tool. It helps firms:
-
Track All Project Costs with real-time accuracy
-
Manage Budgets to avoid overruns and protect margins
-
Streamline Invoicing and monitor receivables
-
Generate Reports that inform better decisions and highlight opportunities for cost savings
C. How to set up a project accounting system

III. Project Budgeting and Cost Management
Project budgeting and cost management are crucial aspects of project accounting for architectural and engineering firms. Project budgeting involves creating a comprehensive plan that outlines the estimated costs and revenue for a specific project. This includes identifying and estimating expenses such as labor, materials, equipment, subcontractors, and overhead costs. By setting a budget, firms can allocate resources effectively, track expenditures, and ensure that the project remains financially viable. Cost management is the ongoing process of monitoring and controlling project costs to ensure they align with the approved budget. This involves tracking actual expenses, comparing them to the budget, and identifying any variances. Effective cost management enables firms to make informed decisions, address cost overruns promptly, and optimize resource allocation to achieve project objectives within the allocated budget. By implementing robust project budgeting and cost management practices, architectural and engineering firms can enhance financial control, improve project profitability, and mitigate financial risks.

A. How to create a project budget
B. Best practices for managing project costs
Controlling project costs isn’t just about staying on budget—it’s about protecting margins, managing resources wisely, and making informed decisions as work progresses. Here’s how to do it right:
1. Plan With Precision
- Define the Scope Clearly to avoid costly scope creep.
- Build a Detailed Budget by breaking costs into categories like labor, materials, and overhead.
- Include Contingencies (typically 10%) for the unexpected.
- Allocate Resources Strategically based on skill, cost, and availability.
2. Estimate and Track Costs Accurately
- Use Proven Estimation Methods like bottom-up, parametric, or analogous techniques.
- Set a Clear Cost Baseline to measure performance.
- Monitor in Real Time using reliable software to track actuals against budget.
- Leverage Earned Value Management (EVM) to understand cost and schedule performance.
3. Control Costs Proactively
- Review Budgets Regularly and identify cost variances early.
- Analyze Variances to understand root causes.
- Take Corrective Action—adjust scope, reassign resources, or shift priorities as needed.
- Use Formal Change Control to manage scope and budget updates.
4. Communicate and Collaborate
- Engage Stakeholders with clear, timely cost updates.
- Keep Your Team in the Loop on budget expectations and progress.
- Partner With Clients to manage scope or funding changes collaboratively.
5. Learn and Improve
- Conduct Post-Project Reviews to identify cost management lessons.
- Train Your Team on cost control techniques.
- Use the Right Tools to automate tracking and improve visibility.
C. How to track and report project cost
IV. Guide to Project Billing and Invoicing
Project billing and invoicing is a critical component of project accounting for architectural and engineering firms. It involves generating accurate and timely invoices for the services provided or work performed on a specific project. The invoices typically outline the scope of work, project milestones, billing rates, and payment terms. Effective project billing ensures that clients are billed accurately and promptly, facilitating timely cash flow for the firm. It is important to track and record all billable expenses and hours worked to ensure that invoices are comprehensive and reflect the true value of the services rendered. Proper project invoicing not only helps in maintaining transparent communication with clients but also minimizes disputes and delays in payment. By implementing efficient project billing and invoicing practices, firms can streamline their financial operations, improve cash flow, and foster strong client relationships.
A. Best practices for project invoices
Creating clear, timely, and professional invoices is critical to maintaining cash flow and client trust. Here's how to make your project invoicing process smooth, consistent, and effective:
1. Set Expectations Early
-
Define payment terms (due dates, methods, late fees) before work begins.
-
Agree on a billing schedule—monthly, milestone-based, or end-of-project.
-
Outline what will be billed and tie it back to the project scope.
2. Use Professional, Consistent Templates
-
Include your logo, contact info, client details, invoice number, itemized charges, and total.
-
Use consistent formatting for every invoice.
-
Consider invoicing tools for polished templates and automation.
3. Track Hours and Expenses Accurately
-
Use time-tracking tools to log billable hours.
-
Keep receipts and records of reimbursable project costs.
4. Send Invoices Promptly
-
Don’t wait—send invoices as soon as work is complete or a milestone is reached.
-
Email delivery or invoicing software speeds things up and provides tracking.
5. Clarify Payment Terms on Every Invoice
-
Clearly state the due date.
-
List accepted payment methods (bank transfer, credit card, online).
-
Include late payment terms to encourage timely responses.
6. Offer Convenient Payment Options
-
Online payments reduce friction.
-
Give clients multiple options—ACH, credit card, etc.
7. Follow Up Professionally
-
Send friendly reminders before and after the due date.
-
Have a system for escalating overdue invoices if needed.
- Project invoicing from Microsoft Dynamics
B. How to manage project billing and payments
Successful project billing isn’t just about getting paid—it’s about setting clear expectations, choosing the right billing model, and maintaining consistent communication throughout the project. When done well, billing strengthens client trust, improves cash flow, and reduces friction.
Here’s how to do it right:
1. Start with Clear Scope and Terms
-
Spell it out in the contract: Define project scope, billing method, payment schedule, and how changes will be handled.
-
Keep communication flowing: Check in regularly with clients about progress, scope changes, and billing expectations.
2. Choose the Right Billing Method
Not every project should be billed the same way. Match the billing model to the scope, complexity, and client relationship:
-
Fixed-Price
Predictable for clients, higher potential margin for you—but risky if scope isn’t tightly defined. -
Time and Materials (T&M)
Flexible and transparent, ideal for evolving projects. Requires disciplined time tracking. -
Milestone-Based
Ties payments to deliverables. Great for managing cash flow and building trust over longer timelines. -
Retainer
Recurring, fixed payments for ongoing access. Supports predictability on both sides. -
Cost-Plus
Bills actual costs + a fee or percentage. Offers clarity but can trigger fee disputes. -
Unit-Based
Bills per unit of work (e.g., per square foot, per hour). Useful for measurable, repeatable deliverables.
3. Implement an Effective Billing Process
-
Track time and costs accurately with project billing software.
-
Invoice promptly and include all agreed details.
-
Offer flexible payment options (ACH, credit card, online portals).
-
Manage scope changes formally, with documented approvals.
-
Review project data regularly to catch issues early.
4. Follow Billing Best Practices
-
Communicate often about billing expectations and status.
-
Be consistent and timely with invoices—don’t let delays become your bottleneck.
-
Reinforce payment terms—include due dates, late penalties, and early-pay incentives.
-
Use billing software to automate, track, and streamline the process.
C. How to handle disputes and late payments

V. Project Financial Reporting and Analysis
Project financial reporting is a vital aspect of project accounting for architectural and engineering firms. It involves generating accurate and comprehensive reports that provide a clear overview of the financial performance of individual projects. These reports typically include information such as project costs, revenues, profitability, and variances from the budget. Project financial reporting enables firms to evaluate the financial health of each project, assess its progress, and make informed decisions based on real-time financial data. By analyzing project financial reports, firms can identify areas of concern, take corrective measures, and optimize resource allocation to maximize profitability. Effective project financial reporting provides transparency and accountability, enabling stakeholders to assess the financial viability and success of ongoing projects. It also assists in fulfilling reporting requirements for clients, investors, and regulatory authorities. By leveraging project financial reporting, architectural and engineering firms can improve financial control, make data-driven decisions, and achieve greater project success.

A. How to create financial reports for projects
B. How to analyze project financial data
C. How to use project financial data to make informed business decisions
To make smarter decisions, don’t just collect data—use it strategically.
- Start by defining clear business objectives, then identify the financial data that matters most—project costs, margins, burn rates, or profitability by phase.
- Next, analyze for trends and patterns that reveal what’s working (and what’s not). Use dashboards or visual reports to clarify the story behind the numbers.
- Finally, translate those insights into concrete actions—whether it’s adjusting pricing, reallocating resources, or refining project scopes—and track the results over time.
VI. Guide to Project Accounting Software
Project accounting software helps architectural and engineering firms streamline and manage their project finances effectively. Unlike regular accounting software, which focuses on general financial management, project accounting software is specifically designed to meet the unique needs of project-based businesses. It offers features and functionalities tailored to project tracking, budgeting, cost management, billing, and financial reporting. With specialized project accounting software, firms can easily create project budgets, track project costs, generate invoices, and monitor financial performance in real-time. These software solutions provide a centralized platform for managing project finances, allowing for better visibility, control, and accuracy.
In addition to specialized project accounting software, firms can also leverage additional plugins and tools to enhance their project accounting capabilities. These plugins and tools can integrate with existing software and provide additional functionalities such as time tracking, expense management, resource planning, and project collaboration. They offer automation, data synchronization, and customized reporting features that further streamline project accounting processes and improve efficiency. By utilizing project accounting software along with relevant plugins and tools, architectural and engineering firms can optimize their financial management, improve project profitability, and make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date financial data.
A. Common Accounting Software Packages
Unfortunately, most common accounting software packages are not well suited to project accounting.
- QuickBooks Enterprise
- Xero Accounting
- Microsoft Dynamics 365
- Sage Intactt
B. Specialized Project Accounting Packages
Purpose-built software packages for project accounting are best suited for most engineering, architecture, and construction firms.
- Deltek Ajera ERP Software for Architecture & Engineering
- Microsoft Dynamics 365
- Sage Intactt Project Finance Module
- Monograph Project Management software for Architects and Engineers
- NetSuite Project Management
- BQE CORE

Your Next Steps on the Path to Peak Project Performance
You now have a full roadmap—from understanding the fundamentals of project accounting and budgeting to mastering billing, financial reporting, and software selection. Here's how to take action:
-
Assess Your Foundation
Identify which parts of your project accounting are working—and where gaps remain. Whether it’s unclear billing structures, inconsistent cost tracking, or lack of real-time data, missing the mark here could mean missed profit opportunities. -
Choose a Starting Point
Pinpoint a single area to improve first: project budgeting practices, timely invoicing, expense allocation, or financial dashboards. Start small, make it meaningful, and build momentum. -
Leverage the Right Tools & Guidance
Use tailored software—like Ajera, NetSuite, or QuickBooks—together with practical workflows to automate the heavy lifting. And if you're not sure where to begin, professional support (like project accounting coaching or outsourced bookkeeping) can help remove the strain—and accelerate results. -
Make Visibility Your Advantage
Unlike traditional accounting, project accounting shines a light on the profitability of each engagement. When you’re able to track costs, margins, and billing at the project level, you’re empowered to make real-time decisions that protect profit and optimize your performance. -
Reinvest in Your Process
At the close of every project, conduct a “lessons learned” session. Update your budgets, billing models, and reporting templates based on those insights. Repeat this cycle to sharpen your financial processes—and your profitability.

Ready to Get Started?
Project accounting isn't just a better way to track numbers, it’s the way forward for firms that want to grow, improve margins, and win better projects with less risk.
At Summit Business Advisors, we help A/E and professional services firms put project accounting into practice - building the right systems, reports, and workflows that support growth without adding stress.
Let’s build your project financial operating system together.
Schedule a consultation today and discover how clarity, control, and profitability can become the steady rhythm of your business.
- The Summit Business Advisors Team
Your path to the summit starts now with knowing your score
With Summit Business Advisors, project-based businesses have real-time visibility into their performance and can make data-driven decisions that drive results.
✓ Profit First
✓ Utilization rate, and
✓ Net revenue per employee

